Defiition:
Plant hormones or Phytohormones may be defined as an
"an organic substance produced naturally in plants which control growth
and other physiological functions at a site away from its place of
synthesis". Thimann (1948) proposed the term phytohormones.
As these hormones are synthesis by plants, they are also
called phytohormones.
Phytohormones
are active in small concentrations. They are capable of influencing
physiological activities leading promotion, inhibition and modification of
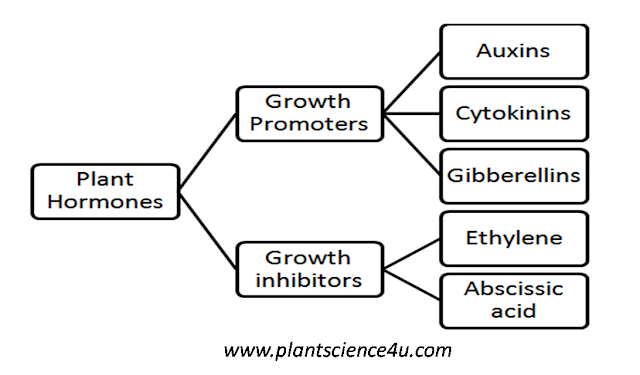
growth. These growth regulatory substances are generally grouped under five
major classes, namely Auxins, gibbellins, cytokinins, ethylene and abscisic
acid.
I.Growth Promoting Hormones:
II. Growth Inhibiting Hormones:
Auxin:
Germinating seeds, stem tips, root tips, leaves, leaf buds
Dominanace
of terminal bud, elongation of stem cells, growth of lateral roots, growth of
plumule and radical, Production of female flowers.
Cytokinins:
Produced at the tips of the root and transported through xylem to different
part of the plant.
Accelerating
cell growth and cell division, germination of seeds, preventing dropping of
flowers and leaves.
Gibberellins:
Germinating seed, embryo, buds, tender leaves, stem and root tips.
Germination
of seeds, breaking down of stored food in germinating seeds, sprouting of
leaves, elongation of stem, cell division, growth.
Ethylene: Produced in roots and diffuse to other part of the plant.
Prevents cell division, causes maturation and ripening of leaves ad fruit.
Abscisic acid: Produced in mature leaves and transported to other plant parts.
Prevents cell division and cell growth, causes the dropping of mature leaves and ripe fruits helps in the dormancy of seeds and buds. III. Other Growth Regulators
- Florigen
- Vernalin
- Brassinosteroids
- Caulines
- Morphactins