Systematic Position
Division: SphenophytaClass: Calamopsida
Family: Equisitaceae
Genus: Equisetum (Horse tails, Scouring rushes) Only living member
Species: Common species include E. arvense (road side), E. debile (river side)Habitat: grows in swampy soil along river side or sandy road sides
Habit: Bushy, perennial herbs
Equisetum: Plant body
Equisetum: Plant body
- Sporophytic plant body
- Differentiated into root, stem and leaves
- Creeping or erect plant body
- Stem: consist of underground rhizome and upright green aerial branches.
- Jointed stem with nodes and internodes, internodes with longitudinal ridges and furrows and hollow interior
- Silica deposits in stem make it rough (Scouring rushes)
- Leaves: nodes with small, sessile microphyllous scale leaves in whorls
- Function: photosynthesis
- Fertile branches bear strobili after some vegetative growth
- Roots: Adventitious roots arise from the nodes of rhizome
- Other features: Homosporous nature, Eusporangiate
Equisetum Stem Anatomy T.S
Vegetative Reproduction: Fragmentation of rhizome, Tubers formed on rhizome
- Equisetum is homosporous and Eusporangiate
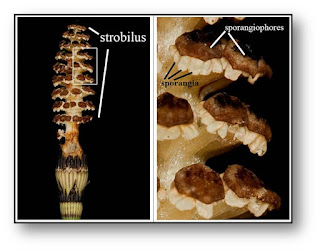
- Strobili are borne terminally and singly on aerial fertile branches.
- Strobilus consists of a central axis on which stalked sporangiophores with sporangium are arranged in whorls
Sporangiophore
· Umbrella shaped structure with a slender stalk and a hexagonal peltate disc
· The underside of peltate disc bears variable number of sac like sporangia
· The number of sporangia in each sporangiophore may vary from 5-10
· Sporangium consists of a 2 cell thick wall, with large number of homosporous spores. Dehiscence along longitudinal slit. Spores are dispersed by wind with the help of elaters
Spores and Elators
• Spores are Green, large, uninucleate, spherical, chloroplast containing structures with exine, intine and outermost epispore
• Elaters are spirally coiled , spoon shaped hygroscopic structures formed from epispore of haploid spore
• Each spore has 4 spirally arranged hygroscopic elaters
• Function: helps in dehiscence of sporangium and spore dispersal
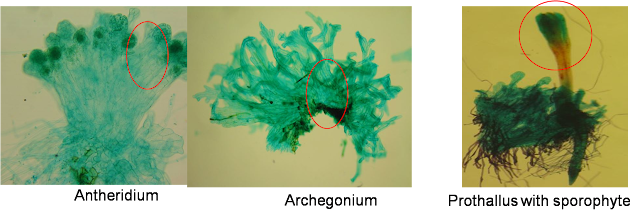
- Spores falling on suitable substratum germinate to form green prothallus with rhizoids for fixation.
- Prothallus consists of a basal disc and number of green vertical lobes.
- Monoecious or bisexual: both antheridia and archegonia are present.
- Antheridia may occur on vertical lobes or basal disc embedded.
- Antheridium produces 256-512multiflagellate, spirally coiled spermatozoids.
- Archegonia flask shaped structures at the base of vertical lobes.
- Fusion forms embryo which give rise to new plant.